
Spatial trasncriptomics
Spatial transcriptomics (10x Genomics Visium ) of mouse brain from a spatial object recognition training experiment
Dataset Overview
GSE201610: 10x Genomics Visium spatial transcriptomics of mouse brain from a spatial object recognition (SOR) training experiment
Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
Organism | Mus musculus (mouse) |
Tissue | Brain sagittal sections |
Platform | 10x Visium + Illumina NovaSeq 6000 |
Samples | 6 total: 3 Home-cage controls (HC1–HC3) + 3 SOR-trained (SOR1–SOR3) |
Spots/Sample | 2,550–2,936 per section |
Genes | 32,285 total |
GEO Accession | GSE201610 |
Cell Types | Not pre-annotated; identified through unsupervised analysis |
Analyses Performed
Unsupervised Spatial Clustering (Single Sample: HC1)
Method: PCA + K-means clustering (k=12)
Output: 12 spatial clusters with anatomically-defined regions
Key Finding: Successfully identified oligodendrocytes, neurons, choroid plexus, ependymal cells, and stromal regions with canonical marker genes
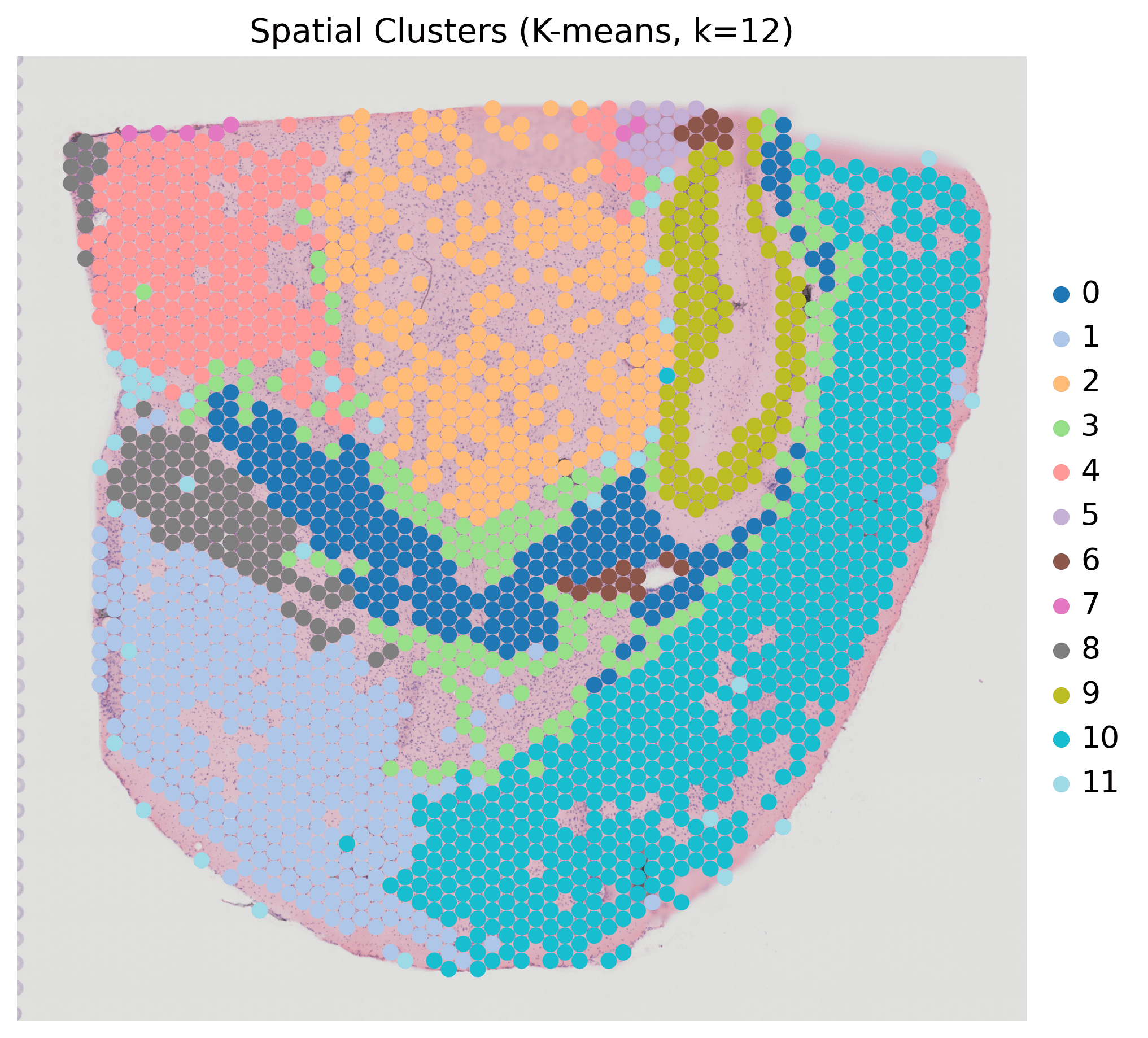
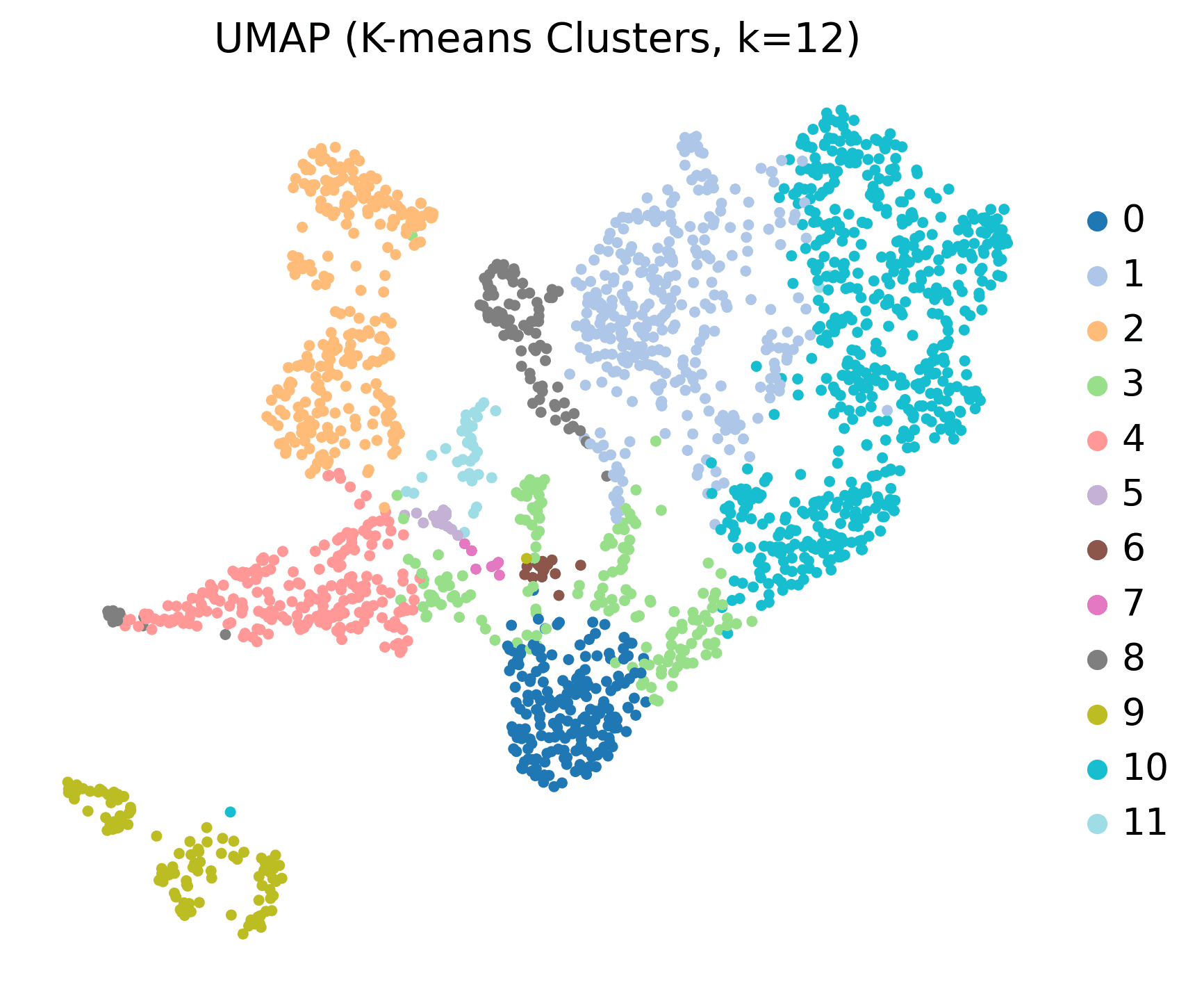
Pan-Sample Clustering (All 6 Samples)
Method: Quality filtering → SCTransform → Louvain clustering (resolution 0.5)
Retention: 10,839 spots (66% of 16,451 total)
Output: 18 anatomically coherent spatial regions
Marker Genes: 16,743 significantly differentially expressed genes across regions
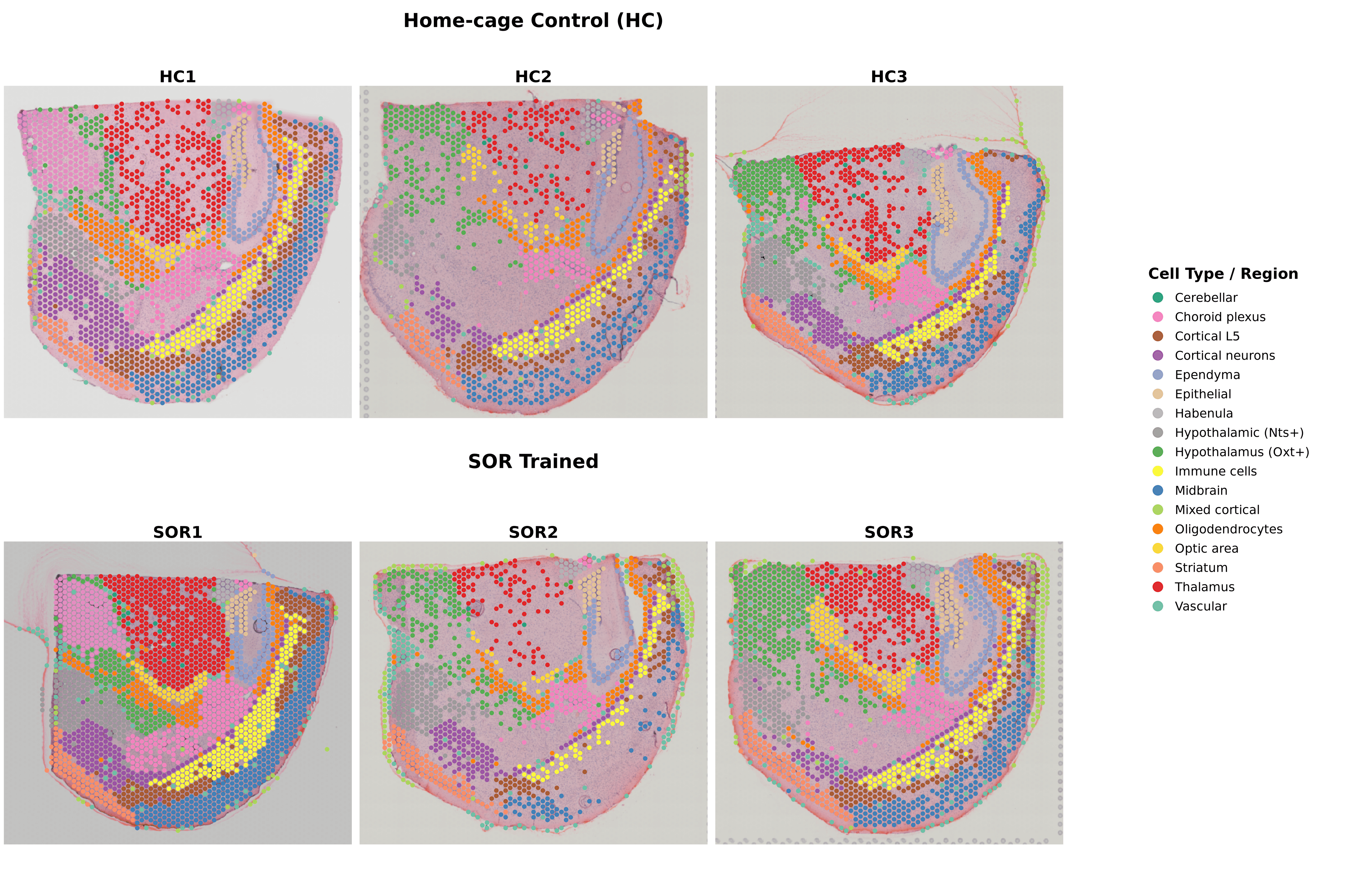
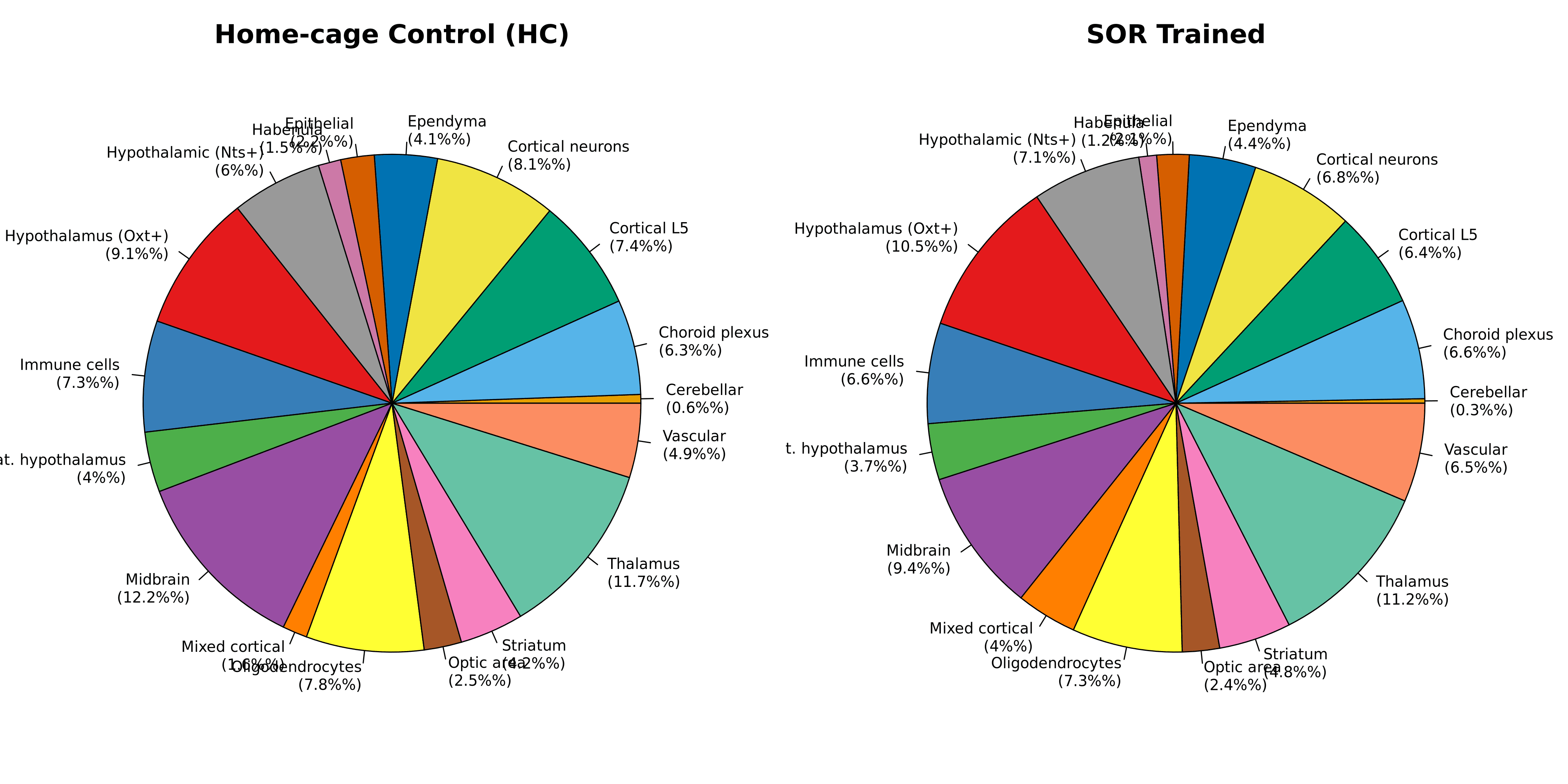
Condition Comparison: HC vs SOR (Proportional Analysis)
Comparison: Home-cage Control (n=3) vs SOR-trained (n=3)
Key Findings:
Thalamus: 11.7% (HC) vs 11.2% (SOR) — minimal change
Midbrain: 12.2% (HC) vs 9.4% (SOR) — −2.8% in SOR (dopaminergic/serotonergic circuits)
Hypothalamus (Oxt+): 9.1% (HC) vs 10.5% (SOR) — +1.4% in SOR
Mixed Cortical: 1.6% (HC) vs 4.0% (SOR) — +2.4% in SOR (potential learning plasticity)
Overall: Anatomical architecture highly conserved across conditions
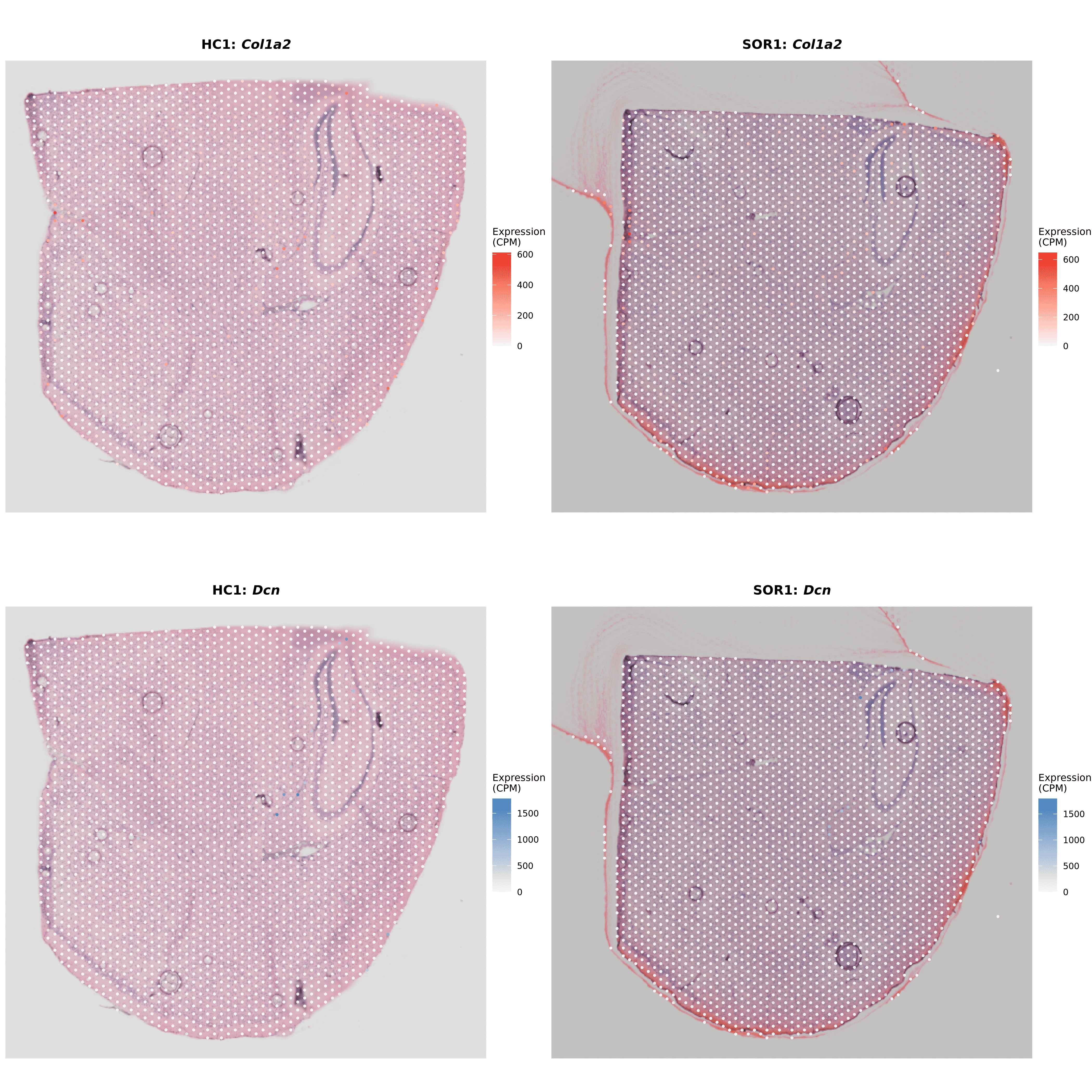
Meninges/Vasculature Spatial Localization (HC1 vs SOR1)
Markers Used: Col1a2, Dcn, Vtn, Col1a1, Col3a1
HC1 Results: 83 meningeal spots (3.12% of tissue), concentrated at periphery
SOR1 Results: 71 meningeal spots (2.78% of tissue)
Key Finding: Meningeal/vascular compartment is structurally preserved between conditions

Key Biological Insights
Intact Brain Architecture: Unsupervised clustering faithfully recapitulates known mouse brain anatomy with clear demarcation of major structures (thalamus, midbrain, cortex, hypothalamus, white matter, choroid plexus)
Training-Induced Compositional Shifts:
Midbrain reduction in SOR suggests potential modulation of dopaminergic/serotonergic circuits
Cortical increase in SOR may reflect learning-associated plasticity
Overall effect sizes are modest (<3% absolute change), requiring larger cohorts for statistical validation
Preserved Stromal/Vascular Compartment: Meningeal and vascular structures remain structurally similar between HC and SOR conditions
Recommended Follow-Up Analyses
Reference-based deconvolution: Apply RCTD or Cell2location with Allen Brain Atlas scRNA-seq for higher cell type resolution
Statistical testing: Formal compositional data analysis (ALDEx2, scCODA) for differential abundance
Spatial differential expression: Identify genes with condition-dependent expression within specific brain regions
Pathway enrichment: Characterize functional programs in regions showing compositional shifts
Larger sample size: Current n=3 per group limits statistical power; recommend n≥5 for robust conclusions


